Figure 12 A DNA strand, bases, nucleotides, genes, and a chromosome (a) A
The DNA strand of bases is a template (model) for the replication of DNA
Each DNA strand is composed of a sequence of bases connected
DNA.gif
File:Dna strand3.png
Model of DNA strand on
Next, the mRNA is chopped up and removed, and the DNA strand is used to make

formed by hydrogen bond interaction of two separate DNA strands.
(DNA ligase is the same enzyme used to bond DNA strands together) DNA
The nitrogenous bases on the two strands of DNA pair up,
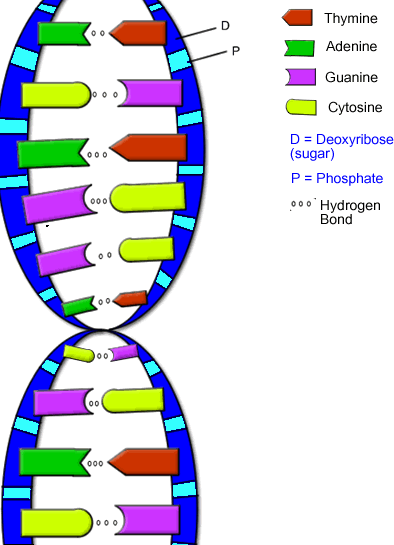
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) consists of two sugar-phosphate strands forming
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) consists of two sugar-phosphate strands forming
DNA that will base pair with the following strand of
Structure of DNA
This picture shows how DNA bases are stacked together along the double helix
DNA polymerase primes the strand, adds base pairs, and repairs damages
DNA and its building blocks.
Figure 12 A DNA strand, bases, nucleotides, genes, and a chromosome (a) A
A typical DNA strand in our cells can be 50
yet been clarified) to the second DNA strand (non-covalent, n-strand),
No comments:
Post a Comment